endocannabinoid system
A simple guide to how it all works
Medical cannabis is only able to affect our bodies because we have a biological system that interacts and reacts with its active compounds.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) plays a role in regulating a number of our everyday and essential functions and is comprised of three core components: endocannabinoids, receptors, and enzymes.
the components of the endocannabinoid system:
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids are molecules made by your body. They are similar to cannabinoids but are produced within you.
Receptors
These receptors are found throughout your body. Endocannabinoids bind to these receptors and signal to the ECS to take action.
Enzymes
Enzymes have the task of breaking down endocannabinoids once they have carried out their function.
Why is the ECS so vital to our health?
Many of the vital functions that the ECS helps regulate are vital in maintaining homeostasis. Homeostasis refers to the ability to maintain relative internal stability regardless of external factors and pressures. All living organisms must achieve and maintain homeostasis to ensure their survival.
how does the ECS ensure homeostasis?
The ECS uses cannabinoids and cannabinoids receptors to help us maintain homeostasis. These receptors are found throughout our immune and central and peripheral nervous systems.
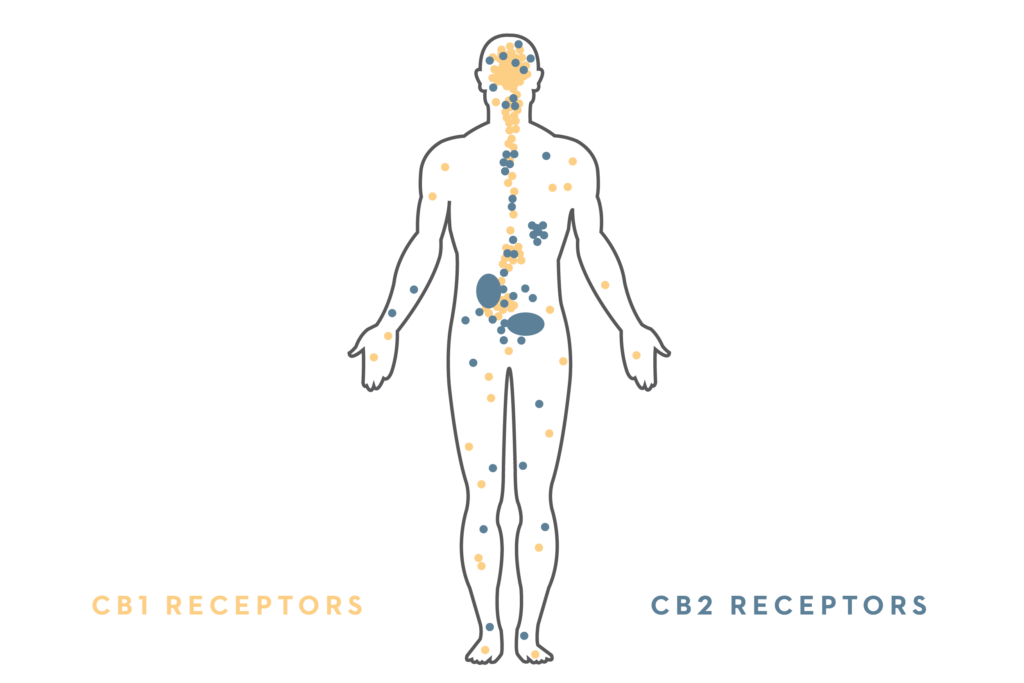
When the ECS detects an imbalance the body produces endocannabinoids to interact with the cannabinoid receptors. This interaction causes a chemical response that helps us get back to homeostasis. The most studied cannabinoid receptors are the Cannabinoid-1 and Cannbinoid-2 receptors.
While the body can produce cannabinoids on demand, there are instances in which the cannabinoids produced are not enough for the ECS to work properly. There is growing evidence that supplementing the ECS with phytocannabinoids (cannabinoids derived from plant life) can help the ECS function properly and improve health and quality of life.
CB1 Receptors
CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain, central nervous system, lungs, liver, and kidneys. One of the most important functions performed by CB1 receptors is to regulate the release of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and glutamate.
CB2 Receptors
CB2 receptors are mostly found on immune cells that circulate the body and brain through the bloodstream. CB2 receptors are only present in the brain when the body has inflammation or injury. Along with regulating inflammation CB2 receptor activity also works to ensure cell survival and proliferation.